If the representation type “scroll bar” is chosen for a signal, several settings are available in the “scaling” area.
The following formula is used to calculate scaling:
physical value = (raw value * factor +offset) * unit of measurement
Minimum:
Specifies the minimum value the physical interpretation of the signal value can take. In this example, the minimum value is -50°C.
Maximum:
Specifies the maximum value the physical interpretation of the signal value can take. In the example, this value is +50°C.
Offset:
Specifies an offset to the measured value.
Factor:
Specifies the factor by which the raw value is multiplied to obtain the physical value.
Unit:
Specifies the textual representation of the measurement unit.
Representation of the signal on a panel
Example 1: Signal with simple scaling
Min value |
0 |
Max value |
255 |
Factor |
1 |
Offset |
0 |
Bit length |
8 |
Signed? |
No |
Value in the message data |
||
Physical value |
Decimal |
Hex |
0 |
0 |
0 |
127 |
127 |
7F |
128 |
128 |
80 |
255 |
255 |
FF |
Configuration of example 1:
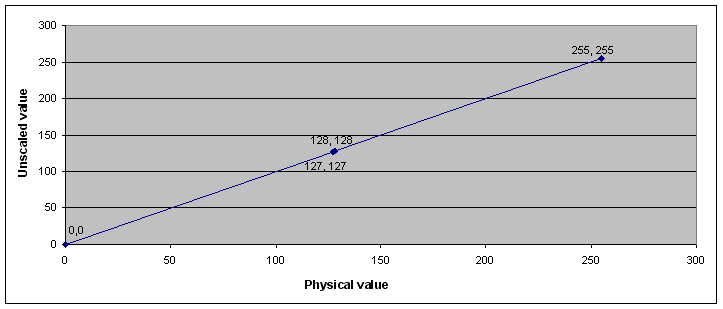
Conversion of physical values into unscaled values
Example 2: Signal with minimum and maximum value and offset
Min value |
-40 |
Max value |
85 |
Factor |
0,5 |
Offset |
-40 |
Bit length |
8 |
Signed? |
No |
Value in the message data |
||
Physical value |
Decimal |
Hex |
-40 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
80 |
50 |
1 |
81 |
51 |
85 |
250 |
FA |
Configuration of example 2:
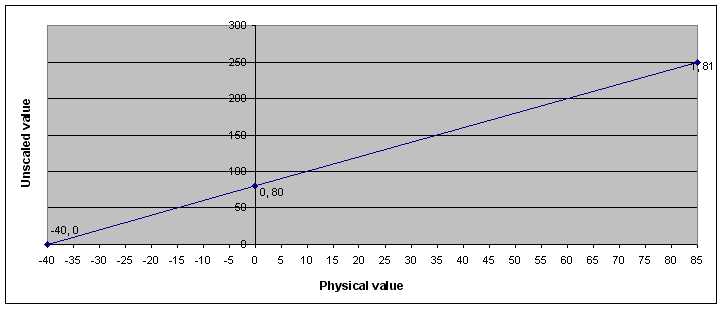
Conversion of physical values into unscaled values
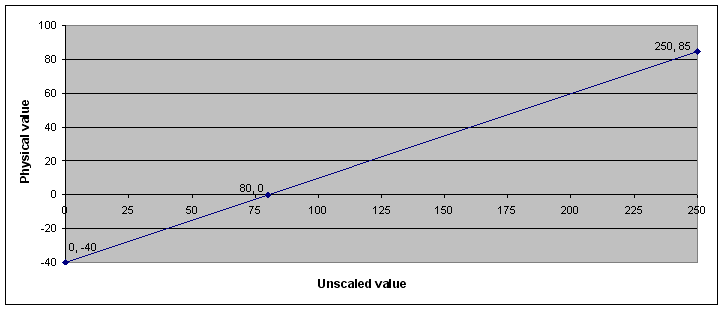
Conversion of unscaled valued into physical values
Example 3: Limited signal using signed values
In this example, the value type is set to “signed”. The most significant bit represents the sign. The result is that the range of raw values is divided into two intervals between which an undefined area can exist.
Min value |
-50 |
Max value |
50 |
Factor |
1 |
Offset |
0 |
Bit length |
8 |
Signed? |
Yes |
Value in the message data |
||
Physical value |
Decimal |
Hex |
-50 |
206 |
CE |
-1 |
255 |
FF |
0 |
0 |
0 |
50 |
50 |
32 |
Configuration of example 3:
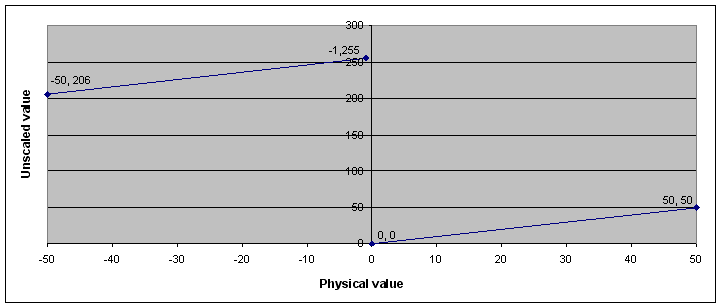
Conversion of physical values into unscaled values
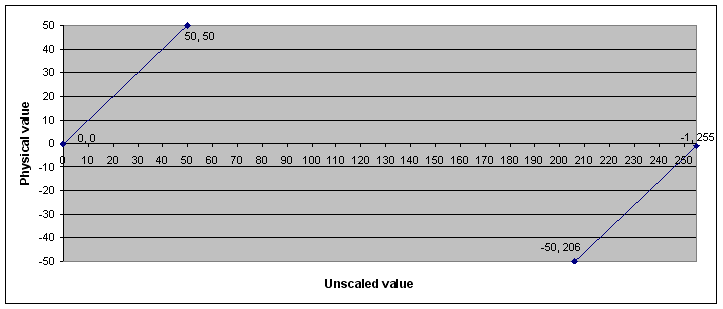
Conversion of unscaled values into physical values